个人笔记
SongPinru 的小仓库
Flink
- 使用Intellij IDEA创建一个Maven新项目
- 勾选
Create from archetype,然后点击Add Archetype按钮 GroupId中输入org.apache.flink,ArtifactId中输入flink-quickstart-scala,Version中输入1.10.0,然后点击OK- 点击向右箭头,出现下拉列表,选中
flink-quickstart-scala:1.10.0,点击Next Name中输入FlinkTutorial,GroupId中输入com.atguigu,ArtifactId中输入FlinkTutorial,点击Next- 最好使用IDEA默认的Maven工具:Bundled(Maven 3),点击
Finish,等待一会儿,项目就创建好了
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
//默认使用方式,自动判断执行环境
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setBufferTimeout(timeoutMillis)//控制缓冲区延迟
//手动指定,本地环境
val localEnv: StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironment()
//手动指定,集群环境
val remoteEnv = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createRemoteEnvironment()
启动yarn-session
./yarn-session.sh -n 2 -s 2 -jm 1024 -tm 1024 -nm test -d
#执行任务
./flink run -c com.wc.StreamWordCount FlinkTutorial-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar --host lcoalhost –port 7777
其中:
-n(–container):TaskManager的数量。
-s(–slots): 每个TaskManager的slot数量,默认一个slot一个core,默认每个taskmanager的slot的个数为1,有时可以多一些taskmanager,做冗余。
-jm:JobManager的内存(单位MB)。
-tm:每个taskmanager的内存(单位MB)。
-nm:yarn 的appName(现在yarn的ui上的名字)。
-d:后台执行。
不启动yarn-session,直接执行job
./flink run –m yarn-cluster -c com.wc.StreamWordCount FlinkTutorial-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar --host lcoalhost –port 7777
Flink Source
从内存的Source
- 从元素中创建:env.fromElements()
- 从集合中创建:env.fromCollection()
//从元素中创建
val stream2: DataStream[SourceReading] = env.fromElements(
SourceReading("source_7", 1586575388360l, 66.95983984624809),
SourceReading("source_8", 1586575388360l, 66.41729455533279),
SourceReading("source_9", 1586575388360l, 66.39501261428823),
SourceReading("source_10", 1586575388360l, 62.635008022112174)
)
//从集合中创建
val stream3: DataStream[SourceReading] = env.fromCollection(
List(SourceReading("source_7", 1586575388360l, 66.95983984624809),
SourceReading("source_8", 1586575388360l, 66.41729455533279),
SourceReading("source_9", 1586575388360l, 66.39501261428823),
SourceReading("source_10", 1586575388360l, 62.635008022112174)))
从文件的Source
val stream = env.readTextFile(filePath)
流式Source
Socket
val socketStream: DataStream[String] = env.socketTextStream("hadoop102",9999,'\n')
Kafka
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.11_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2</version>
</dependency>
val properties = new Properties()
//设置连接kafka的属性
properties.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092")
properties.setProperty("group.id", "consumer-group")
properties.setProperty("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
properties.setProperty("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer")
properties.setProperty("auto.offset.reset", "latest")
//kafka2.0之后取消了scala的api,直接使用java的(即不用加011)
val stream3 = env.addSource(new FlinkKafkaConsumer011[String]("sensor", new SimpleStringSchema(), properties))
自定义Source
- 继承RichParallelSourceFunction
- 实现两个方法run和cancel
- 把数据放入context
class SendSource extends RichParallelSourceFunction[SourceReading]{
var running=true
override def run(sourceContext: SourceFunction.SourceContext[SourceReading]): Unit = {
val random = new Random()
//无限循环,产生数据流
while (running) {
for (i <- 1 to 10) {
val ts: Long = new Date().getTime
val sourceReading = SourceReading("source_" + i, ts, 65 + random.nextGaussian()*20)
//核心,数据放入上下文
sourceContext.collect(sourceReading)
}
Thread.sleep(100)
}
}
//取消函数,打断循环
override def cancel(): Unit = {
running=false
}
}
Transformation
转换算子
基本转换算子
| 算子 | extend |
|---|---|
| map | MapFunction[T] |
| flatmap | FlatMapFunction[T,R] |
| filter | FilterFunction[T] |
KeyBy&滚动聚合
val keyedStream: KeyedStream[SourceReading, Tuple] = stream1.keyBy(1)
- sum():在输入流上对指定的字段做滚动相加操作。
- min():在输入流上对指定的字段求最小值。
- max():在输入流上对指定的字段求最大值。
- minBy():在输入流上针对指定字段求最小值,并返回包含当前观察到的最小值的事件。
- maxBy():在输入流上针对指定字段求最大值,并返回包含当前观察到的最大值的事件。
- reducer():聚合操作
多流转换
Connect与Union区别:
-
Union之前两个流的类型必须是一样,Connect可以不一样,在之后的coMap中再去调整成为一样的。
-
Connect只能操作两个流,Union可以操作多个。
Union
val tokyoStream: DataStream[SensorReading] = ...
val rioStream: DataStream[SensorReading] = ...
val allCities: DataStream[SensorRreading] = parisStream.union(tokyoStream, rioStream)
Connect
// first stream
val first: DataStream[Int] = ...
// second stream
val second: DataStream[String] = ...
// connect streams
val connected: ConnectedStreams[Int, String] = first.connect(second)
COMAP和COFLATMAP
//使用
stream1.connect(stream1).map(new MyMapFunction)
//CoMap
class MyMapFunction extends CoMapFunction[SourceReading,SourceReading,SourceReading]{
override def map1(in1: SourceReading): SourceReading = ???
override def map2(in2: SourceReading): SourceReading = ???
}
//CoFlatMap
class MyCoFlatMap extends CoFlatMapFunction[SourceReading,SourceReading,SourceReading]{
override def flatMap1(value: SourceReading, out: Collector[SourceReading]): Unit = ???
override def flatMap2(value: SourceReading, out: Collector[SourceReading]): Unit = ???
}
分布式转换算子(shuffle)
Random
随机数据交换由DataStream.shuffle()方法实现。shuffle方法将数据随机的分配到下游算子的并行任务中去。
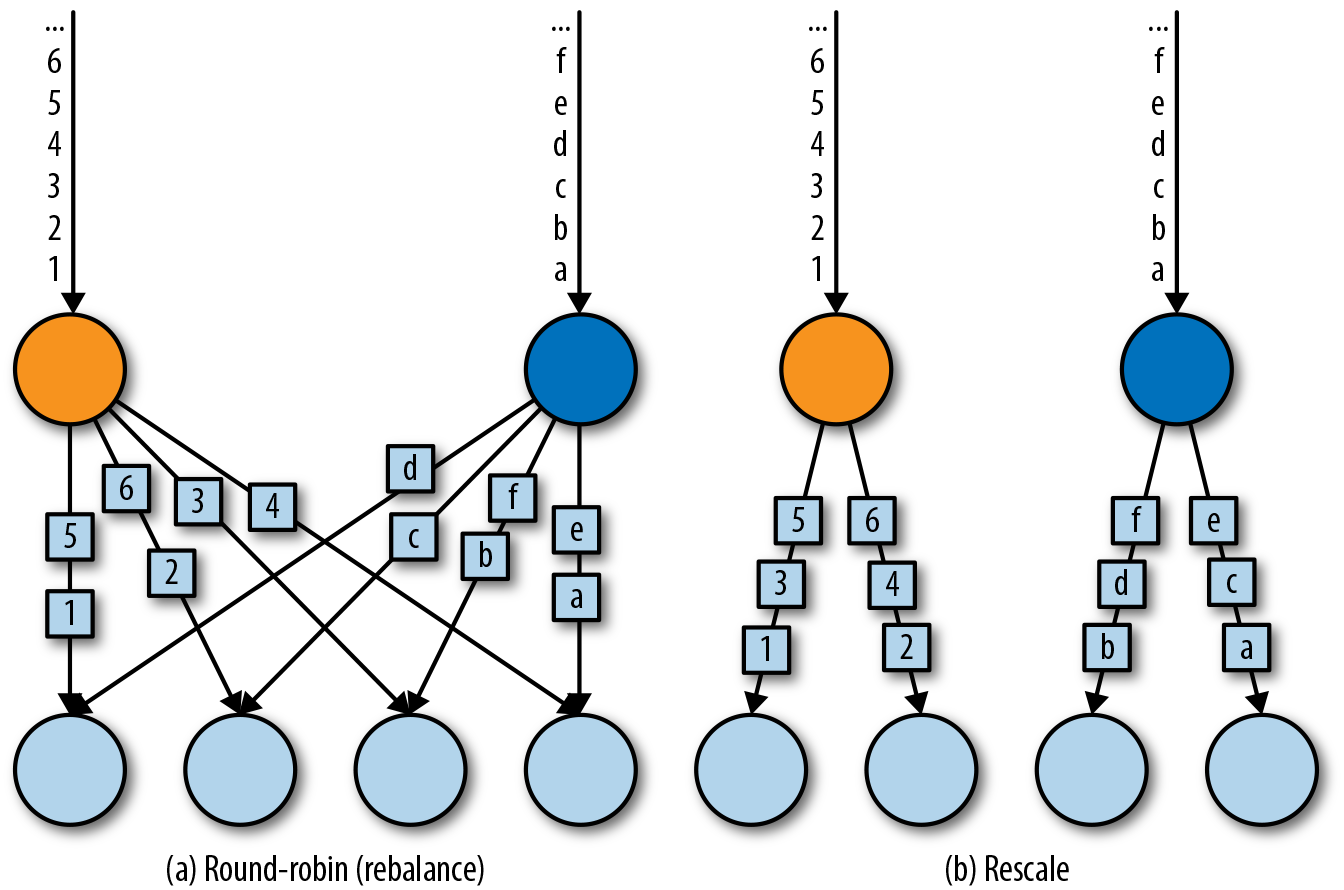
Round-Robin
rebalance()方法使用Round-Robin负载均衡算法将输入流平均分配到随后的并行运行的任务中去。图5-7为round-robin分布式转换算子的示意图。
Rescale
rescale()方法使用的也是round-robin算法,但只会将数据发送到接下来的并行运行的任务中的一部分任务中。
rebalance()和rescale()的根本区别在于任务之间连接的机制不同。rebalance()将会针对所有发送者任务和所有接收者任务之间建立通信通道,而rescale()仅仅针对每一个任务和下游算子的一部分子并行任务之间建立通信通道。rescale的示意图为图5-7。
Broadcast
broadcast()方法将输入流的所有数据复制并发送到下游算子的所有并行任务中去。
Global
global()方法将所有的输入流数据都发送到下游算子的第一个并行任务中去。这个操作需要很谨慎,因为将所有数据发送到同一个task,将会对应用程序造成很大的压力。
Custom
当Flink提供的分区策略都不适用时,我们可以使用partitionCustom()方法来自定义分区策略。这个方法接收一个Partitioner对象,这个对象需要实现分区逻辑以及定义针对流的哪一个字段或者key来进行分区。下面的例子将一条整数流做partition,使得所有的负整数都发送到第一个任务中,剩下的数随机分配。
val stream: DataStream[(Int)] = ...
stream.partitionCustom(myPartitioner, 0)
object myPartitioner extends Partitioner[Int] {
val r = scala.util.Random
override def partition(key: Int, numPartitions: Int): Int = {
if (key < 0) 0 else r.nextInt(numPartitions)
}
}
支持的数据类型
Flink支持Java和Scala提供的所有普通数据类型。最常用的数据类型可以做以下分类:
- Primitives(原始数据类型)
- Java和Scala的Tuples(元组)
- Scala的样例类
- POJO类型
- 一些特殊的类型
富函数(Rich Functions)
当我们使用富函数时,我们可以实现两个额外的方法:
- open()方法是rich function的初始化方法,当一个算子例如map或者filter被调用之前open()会被调用。open()函数通常用来做一些只需要做一次即可的初始化工作。
- close()方法是生命周期中的最后一个调用的方法,通常用来做一些清理工作。
另外,getRuntimeContext()方法提供了函数的RuntimeContext的一些信息,例如函数执行的并行度,当前子任务的索引,当前子任务的名字。同时还它还包含了访问分区状态的方法。
class MyFlatMap extends RichFlatMapFunction[Int, (Int, Int)] {
var subTaskIndex = 0
override def open(configuration: Configuration): Unit = {
subTaskIndex = getRuntimeContext.getIndexOfThisSubtask
// 做一些初始化工作
// 例如建立一个和HDFS的连接
}
override def flatMap(in: Int, out: Collector[(Int, Int)]): Unit = {
if (in % 2 == subTaskIndex) {
out.collect((subTaskIndex, in))
}
}
override def close(): Unit = {
// 清理工作,断开和HDFS的连接。
}
}
Window API
coGroup和join类似,coGroup返回的是两个列表(相同key)
相当于 join.groupby
窗口
- 全窗口:ProcessWindowFunction
- 计数窗口:countWindow
- 时间窗口:timeWindow
- 滚动、滑动
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[SourceReading] = env.addSource(new SendSource).setParallelism(1)
stream.map(sr=>(sr.id,sr.temperature))
.keyBy(_._1)
//.window()
//.ProcessWindowFunction()
//.countWindow(10,5)
//.timeWindow(Time.seconds(10),Time.seconds(5))
//滚动,事件时间
val avgTemp = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(1)))
.process(new TemperatureAverager)
//滚动,机器时间
val avgTemp = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(1)))
.process(new TemperatureAverager)
//滑动,事件时间
val slidingAvgTemp = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.hours(1), Time.minutes(15)))
.process(new TemperatureAverager)
//滑动,机器时间
val slidingAvgTemp = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(SlidingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.hours(1), Time.minutes(15)))
.process(new TemperatureAverager)
//会话窗口:间隔超过gap后为新窗口
val sessionWindows = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(15)))
.process(...)
val sessionWindows = sensorData
.keyBy(_.id)
.window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(15)))
.process(...)
聚合函数
增量聚合函数keyby之后使用
- reducer
- aggregate
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[SourceReading] = env.addSource(new SendSource).setParallelism(1)
stream.map(sr=>(sr.id,sr.temperature))
.keyBy(_._1)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.aggregate(new MyAvgFunction)
.print()
env.execute()
}
class MyAvgFunction extends AggregateFunction[(String,Double),(String,Double,Int),(String,Double)]{
override def createAccumulator(): (String, Double, Int) = {
(null,0.0,0)
}
全局聚合函数
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
env.addSource(new SendSource)
.map(sr=>(sr.id,sr.temperature))
.keyBy(_._1)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.process(new MyProcess)
.print()
env.execute()
}
class MyProcess extends ProcessWindowFunction[(String,Double),(String,Double,Double,Long),String,TimeWindow]{
override def process(key: String, context: Context, elements: Iterable[(String, Double)], out: Collector[(String, Double, Double,Long)]): Unit = {
val windowEnd: Long = context.window.getEnd
// elements.map()
out.collect((key,elements.maxBy(_._2)._2,elements.minBy(_._2)._2,windowEnd))
}
其他窗口api
- 自定义窗口分配器
- 自定义窗口计算触发器(trigger)
- 自定义窗口数据清理功能(evictor)
窗口分配器
WindowAssigner有两个泛型参数:
- T: 事件的数据类型
- W: 窗口的类型
下面的代码创建了一个自定义窗口分配器,是一个30秒的滚动事件时间窗口。
class ThirtySecondsWindows extends WindowAssigner[Object, TimeWindow] {
val windowSize: Long = 30 * 1000L
override def assignWindows(
o: Object,
ts: Long,
ctx: WindowAssigner.WindowAssignerContext): java.util.List[TimeWindow] = {
val startTime = ts - (ts % windowSize)
val endTime = startTime + windowSize
Collections.singletonList(new TimeWindow(startTime, endTime))
}
override def getDefaultTrigger(
env: environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment): Trigger[Object, TimeWindow] = {
EventTimeTrigger.create()
}
override def getWindowSerializer(
executionConfig: ExecutionConfig): TypeSerializer[TimeWindow] = {
new TimeWindow.Serializer
}
override def isEventTime = true
}
触发器(Trigger)
object TriggerExample {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
val stream = env.addSource(new SendSource)
.keyBy(_.id)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.trigger(new MyTrigger)
.process(new MyProcessFunc)
.print()
env.execute()
}
class MyTrigger extends Trigger[SourceReading,TimeWindow] {
var firstSeen: ValueState[Boolean] = _
override def onElement(element: SourceReading, timestamp: Long, window: TimeWindow, ctx: Trigger.TriggerContext): TriggerResult = {
firstSeen= ctx.getPartitionedState(new ValueStateDescriptor[Boolean]("firstseen",Types.of[Boolean]))
if(!firstSeen.value()){
val l: Long = ctx.getCurrentProcessingTime/1000*1000+1000
ctx.registerProcessingTimeTimer(l)
ctx.registerProcessingTimeTimer(window.getEnd)
firstSeen.update(true)
}
TriggerResult.CONTINUE
}
override def onProcessingTime(time: Long, window: TimeWindow, ctx: Trigger.TriggerContext): TriggerResult = {
if(time==window.getEnd){
TriggerResult.FIRE_AND_PURGE
}else{
println(time)
ctx.registerProcessingTimeTimer(time+1000)
TriggerResult.FIRE
}
}
override def onEventTime(time: Long, window: TimeWindow, ctx: Trigger.TriggerContext): TriggerResult = {
TriggerResult.CONTINUE
}
override def clear(window: TimeWindow, ctx: Trigger.TriggerContext): Unit = {
firstSeen.clear()
}
}
class MyProcessFunc extends ProcessWindowFunction[SourceReading,String,String,TimeWindow] {
override def process(key: String, context: Context, elements: Iterable[SourceReading], out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
out.collect(context.currentProcessingTime +"共有"+elements.size+"条数据")
}
}
}
Process Function(Low-Level API)
Flink提供了8个Process Function:(processElement,onTimer)
-
ProcessFunction
- sideOutput
- KeyedProcessFunction
- keyBy 之后使用,每个元素计算
- CoProcessFunction
- connect 之后使用,类似join,每个元素计算
- ProcessJoinFunction
- BroadcastProcessFunction
- KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction
-
ProcessWindowFunction
- window之后使用
- ProcessAllWindowFunction
侧输出 SideOutput
stream.getSideOutput()ctx.output()new OutputTag[String]("name")
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
val stream: DataStream[SourceReading] = env.addSource(new SendSource)
.process(new FreezingMonitor)
val stream2= stream.getSideOutput(new OutputTag[String]("freezing-alarms"))
// stream.print()
stream2.print()
env.execute()
}
class FreezingMonitor extends ProcessFunction[SourceReading,SourceReading]{
override def processElement(value: SourceReading, ctx: ProcessFunction[SourceReading, SourceReading]#Context, out: Collector[SourceReading]): Unit = {
if(value.temperature<32){
ctx.output(new OutputTag[String]("freezing-alarms"),s"${value.temperature} freezing")
}
out.collect(value)
}
}
KeyedProcessFunction
class TempIncreaseAlertFunction extends KeyedProcessFunction[String,SourceReading,String]{
lazy val lastTemp: ValueState[Double] = getRuntimeContext.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor[Double]("last-temp",Types.of[Double]))
lazy val currentTimer: ValueState[Long] = getRuntimeContext.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor[Long]("timer",Types.of[Long]))
//定时器
override def onTimer(timestamp: Long, ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, SourceReading, String]#OnTimerContext, out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
out.collect("传感器id为:" + ctx.getCurrentKey + " 的传感器温度值已经连续1s上升了!")
currentTimer.clear()
}
//每个元素的执行操作
override def processElement(value: SourceReading, ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, SourceReading, String]#Context, out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
val previousTemp: Double = lastTemp.value()
val currentTime: Long = currentTimer.value()
if (previousTemp==0.0||value.temperature<previousTemp){
ctx.timerService().deleteProcessingTimeTimer(currentTime)
currentTimer.clear()
}else if(value.temperature>previousTemp&¤tTime==0){
val timerTime: Long = value.ts+1000
ctx.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(timerTime)
currentTimer.update(timerTime)
}
}
时间语义和Watermark
Timestamps
机器时间[process、source],事件时间
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
//设置时间戳对象(机器时间[process、source],事件时间)
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
// 每隔5秒产生一个水位线
env.getConfig.setAutoWatermarkInterval(5000)
WaterMark
- 一个表示窗口结束的事件
- 计算方式:最大时间戳 - 最大延迟
val readings: DataStream[SensorReading] = env
.addSource(new SensorSource)
.filter(r => r.temperature > 25)
//设置时间戳和水位线
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new MyAssigner())
//没有延迟可用递增
// .assignAscendingTimestamps(_._2)
//官方提供的周期性水位线
/*.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
new BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor[(String, Long)](Time.seconds(10)) {
override def extractTimestamp(t: (String, Long)): Long = t._2
})*/
MyAssigner有两种类型
- AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks
- AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks
以上两个接口都继承自TimestampAssigner。
周期性水位线
class awpe extends AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks[(String,Long)]{
val bound=500l
var maxTS=0l
override def getCurrentWatermark: Watermark = new Watermark(maxTS-bound)
override def extractTimestamp(element: (String, Long), previousElementTimestamp: Long): Long = {
maxTS=element._2.max(maxTS)
element._2
}
}
不规则的水位线
class PunctuatedAssigner extends AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks[SensorReading] {
val bound: Long = 60 * 1000
override def checkAndGetNextWatermark(r: SensorReading, extractedTS: Long): Watermark = {
if (r.id == "sensor_1") {
new Watermark(extractedTS - bound)
} else {
null
}
}
override def extractTimestamp(r: SensorReading, previousTS: Long): Long = {
r.timestamp
}
}
状态和检查点
State
- 富函数(
getRunTimeContext.getState())或者上下文环境中的特殊变量 - valueState
- ListState
object RichFlatMapStateExample {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setParallelism(1)
val stream = env
.addSource(new SendSource)
.keyBy(_.id)
.flatMap(new TemperatureAlertFunction(1.7))
stream.print()
env.execute()
}
class TemperatureAlertFunction(val threshold:Double) extends RichFlatMapFunction[SourceReading,(String,Double,Double)] {
lazy val lasttemp: ValueState[Double] = getRuntimeContext.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor[Double]("lasttemp",Types.of[Double]))
override def flatMap(value: SourceReading, out: Collector[(String, Double, Double)]): Unit = {
val diff: Double = (lasttemp.value()-value.temperature).abs
if(diff>threshold){
out.collect((value.id,value.temperature,diff))
}
lasttemp.update(value.temperature)
}
}
}
CheckPoint
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment()
// 每 1000ms 开始一次 checkpoint
env.enableCheckpointing(1000)
// 高级选项:
// 设置模式为精确一次 (这是默认值)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
// 确认 checkpoints 之间的时间会进行 500 ms
env.getCheckpointConfig.setMinPauseBetweenCheckpoints(500)
// Checkpoint 必须在一分钟内完成,否则就会被抛弃
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointTimeout(60000)
// 如果 task 的 checkpoint 发生错误,会阻止 task 失败,checkpoint 仅仅会被抛弃
env.getCheckpointConfig.setFailTasksOnCheckpointingErrors(false)
// 同一时间只允许一个 checkpoint 进行
env.getCheckpointConfig.setMaxConcurrentCheckpoints(1)
./bin/flink stop \
--savepointPath /tmp-flink-savepoints \
$JOB_ID
./bin/flink run \
--fromSavepoint <savepointPath> \
--allowNonRestoredState ...
相关的配置选项
更多的属性与重置值能在conf/flink-conf.yaml中设置(完整教程请阅读配置)。
| 键 | 默认 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| state.backend | (没有) | 串 | 用于存储和检查点状态的状态后端。 |
| state.backend.async | true | 布尔型 | 选择状态后端是否应在可能且可配置的情况下使用异步快照方法。某些状态后端可能不支持异步快照,或仅支持异步快照,而忽略此选项。 |
| state.backend.fs.memory-threshold | 1024 | 整数 | 状态数据文件的最小大小。所有小于状态块的状态块都以内联方式存储在根检查点元数据文件中。 |
| state.backend.fs.write-buffer-size | 4096 | 整数 | 写入文件系统的检查点流的写缓冲区的默认大小。实际的写缓冲区大小确定为该选项和选项“ state.backend.fs.memory-threshold”的最大值。 |
| state.backend.incremental | false | 布尔型 | 选择状态后端是否应创建增量检查点(如果可能)。对于增量检查点,仅存储与前一个检查点的差异,而不存储完整的检查点状态。某些状态后端可能不支持增量检查点,因此会忽略此选项。 |
| state.backend.local-recovery | false | 布尔型 | 此选项为此状态后端配置本地恢复。默认情况下,本地恢复处于禁用状态。当前,本地恢复仅涵盖键控状态后端。当前,MemoryStateBackend不支持本地恢复,请忽略此选项。 |
| state.checkpoints.dir | (没有) | 串 | 用于在Flink支持的文件系统中存储检查点的数据文件和元数据的默认目录。必须从所有参与的进程/节点(即所有TaskManager和JobManager)访问存储路径。 |
| state.checkpoints.num保留 | 1个 | 整数 | 要保留的最大已完成检查点数。 |
| state.savepoints.dir | (没有) | 串 | 保存点的默认目录。由状态后端用于将保存点写入文件系统(MemoryStateBackend,FsStateBackend,RocksDBStateBackend)。 |
| taskmanager.state.local.root-dirs | (没有) | 串 | config参数定义用于存储基于文件的状态以进行本地恢复的根目录。当前,本地恢复仅涵盖键控状态后端。当前,MemoryStateBackend不支持本地恢复,请忽略此选项 |
默认情况下,状态是保持在 TaskManagers 的内存中,checkpoint 保存在 JobManager 的内存中。为了合适地持久化大体量状态, Flink 支持各种各样的途径去存储 checkpoint 状态到其他的 state backends 上。通过 StreamExecutionEnvironment.setStateBackend(…) 来配置所选的 state backends。
选择
Sink
Kafka
Kafka版本为0.11
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka-0.11_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.10.0</version>
</dependency>
Kafka版本为2.0以上
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.10.0</version>
</dependency>
主函数中添加sink:
val union = high.union(low).map(_.temperature.toString)
union.addSink(new FlinkKafkaProducer011[String]("localhost:9092", "test", new SimpleStringSchema()))
env.execute()
Redis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.bahir</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-redis_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
定义一个redis的mapper类,用于定义保存到redis时调用的命令:
class MyRedisMapper extends RedisMapper[SensorReading] {
override def getCommandDescription: RedisCommandDescription = {
new RedisCommandDescription(RedisCommand.HSET, "sensor_temperature")
}
override def getValueFromData(t: SensorReading): String = t.temperature.toString
override def getKeyFromData(t: SensorReading): String = t.id
}
stream.addSink(new RedisSink[SourceReading](config,new MyRedisMapper()))
env.execute()
ElasticSearch
在主函数中调用:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-elasticsearch6_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.10.0</version>
</dependency>
在主函数中调用:
val httpHosts = new util.ArrayList[HttpHost]()
httpHosts.add(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200))
val esSinkBuilder = new ElasticsearchSink.Builder[SensorReading](
httpHosts,
new ElasticsearchSinkFunction[SensorReading] {
override def process(t: SensorReading, runtimeContext: RuntimeContext, requestIndexer: RequestIndexer): Unit = {
println("saving data: " + t)
val json = new util.HashMap[String, String]()
json.put("data", t.toString)
val indexRequest = Requests
.indexRequest()
.index("sensor")
.`type`("readingData")
.source(json)
requestIndexer.add(indexRequest)
println("saved successfully")
}
})
dataStream.addSink(esSinkBuilder.build())
env.execute()
JDBC自定义sink
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.44</version>
</dependency>
添加MyJdbcSink
class MyJdbcSink() extends RichSinkFunction[SensorReading]{
var conn: Connection = _
var insertStmt: PreparedStatement = _
var updateStmt: PreparedStatement = _
// open 主要是创建连接
override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
super.open(parameters)
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "123456")
insertStmt = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO temperatures (sensor, temp) VALUES (?, ?)")
updateStmt = conn.prepareStatement("UPDATE temperatures SET temp = ? WHERE sensor = ?")
}
// 调用连接,执行sql
override def invoke(value: SensorReading, context: SinkFunction.Context[_]): Unit = {
updateStmt.setDouble(1, value.temperature)
updateStmt.setString(2, value.id)
updateStmt.execute()
if (updateStmt.getUpdateCount == 0) {
insertStmt.setString(1, value.id)
insertStmt.setDouble(2, value.temperature)
insertStmt.execute()
}
}
override def close(): Unit = {
insertStmt.close()
updateStmt.close()
conn.close()
}
}
在main方法中增加,把明细保存到mysql中
dataStream.addSink(new MyJdbcSink())
env.execute()
Table&SQL
table:
POM:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table_2.11</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2</version>
</dependency>
- 字段:
'name
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream = env.addsource
// 基于env创建 tableEnv
//val settings = EnvironmentSettings
// .newInstance()
// .useBlinkPlanner()
// .inStreamingMode()
// .build()
//val tenv: StreamTableEnvironment = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env,settings)
val tableEnv: StreamTableEnvironment = TableEnvironment.getTableEnvironment(env)
// 从一条流创建一张表
val dataTable: Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(stream)
val dataTable: Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream,’id,’timestamp .......)
// 从表变成流
table.toAppendStream[(String,String)]
env.execute()
关于group by
如果使用了 groupby,table转换为流的时候只能用toRetractStream
val dataStream: DataStream[(Boolean, (String, Long))] = table.toRetractStream[(String,Long)]
toRetractDstream得到的第一个boolean型字段标识true就是最新的数据(Insert),false表示过期老数据(Delete)
val dataStream: DataStream[(Boolean, (String, Long))] = table.toRetractStream[(String,Long)]
dataStream.filter(_._1).print()
如果使用的api包括时间窗口,那么窗口的字段必须出现在groupBy中。
val resultTable: Table = dataTable
.window( Tumble over 10.seconds on 'ts as 'tw )
.groupBy('id, 'tw)
.select('id, 'id.count)
关于时间窗口
用到时间窗口,必须提前声明时间字段,如果是Processing Time直接在创建动态表时进行追加就可以。
val dataTable: Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, 'id, 'temperature, 'ps.proctime)
如果是EventTime要在创建动态表时声明
val dataTable: Table = tableEnv.fromDataStream(dataStream, 'id, 'temperature, 'ts.rowtime)
滚动窗口可以使用Tumble over 10000.millis on来表示
val resultTable: Table = dataTable
.window( Tumble over 10.seconds on 'ts as 'tw)
.groupBy('id, 'tw)
.select('id, 'id.count)
SQL
| 窗口标识函数 | 返回类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
TUMBLE_START(time-attr, size-interval) |
TIMESTAMP | 返回窗口的起始时间(包含边界)。例如[00:10, 00:15) 窗口,返回 00:10 。 |
TUMBLE_END(time-attr, size-interval) |
TIMESTAMP | 返回窗口的结束时间(包含边界)。例如[00:00, 00:15]窗口,返回 00:15。 |
TUMBLE_ROWTIME(time-attr, size-interval) |
TIMESTAMP(rowtime-attr) | 返回窗口的结束时间(不包含边界)。例如[00:00, 00:15]窗口,返回 00:14:59.999 。返回值是一个rowtime attribute,即可以基于该字段做时间属性的操作,例如,级联窗口只能用在基于Event Time的Window上。 |
TUMBLE_PROCTIME(time-attr, size-interval) |
TIMESTAMP(rowtime-attr) | 返回窗口的结束时间(不包含边界)。例如[00:00, 00:15]窗口,返回00:14:59.999 。返回值是一个proctime attribute,即可以基于该字段做时间属性的操作,例如,级联窗口只能用在基于Processing Time的Window上。 |
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/62511.html?spm=a2c4g.11186623.6.642.106219f9uFTFtr
CEP
POM:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-cep-scala_${scala.binary.version}</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
- begin
- where
- next
- within
- select:返回一条
- flatselect:返回多条
val loginFailPattern = Pattern.begin[LoginEvent]("begin")
.where(_.eventType.equals("fail"))
.next("next")
.where(_.eventType.equals("fail"))
.within(Time.seconds(10))
val patternStream = CEP.pattern(stream, loginFailPattern)
val loginFailDataStream = patternStream
.select((pattern: Map[String, Iterable[LoginEvent]]) => {
val first = pattern.getOrElse("begin", null).iterator.next()
val second = pattern.getOrElse("next", null).iterator.next()
(second.userId, second.ip, second.eventType)
})
超时事件的处理
val complexResult = patternStream.select(orderTimeoutOutput) {
(pattern: Map[String, Iterable[OrderEvent]], timestamp: Long) => {
val createOrder = pattern.get("begin")
OrderTimeoutEvent(createOrder.get.iterator.next().orderId, "timeout")
}
} {
pattern: Map[String, Iterable[OrderEvent]] => {
val payOrder = pattern.get("next")
OrderTimeoutEvent(payOrder.get.iterator.next().orderId, "success")
}
}
val timeoutResult = complexResult.getSideOutput(orderTimeoutOutput)
complexResult.print()
timeoutResult.print()